When your company lets a large language model (LLM) handle customer data, employee records, or financial reports, you're not just using AI-you're handing it the keys to your most sensitive information. And if you don't have tight access controls and detailed audit trails, you're asking for trouble. In 2024, 68% of enterprises using LLMs suffered at least one data leak. The average cost? Over $4.2 million. This isn’t hypothetical. It’s happening right now.
Why Standard Security Doesn’t Work for LLMs
Traditional security tools were built for databases, APIs, and web apps. They track who logged in, what file was opened, and when a system crashed. But LLMs don’t just access data-they generate it. They rewrite prompts, retrieve information from internal documents, and output answers that didn’t exist before. A simple login log won’t tell you if a model hallucinated a fake patient diagnosis or leaked confidential merger details because someone typed the wrong prompt.That’s why you need something deeper: a system that records every step of an LLM interaction. Not just the final answer. The full context. The prompt. The sources it pulled from. The guardrails it triggered-or ignored. Without this, you can’t prove compliance, investigate breaches, or even understand how your AI made a decision.
What Goes Into a Real Audit Trail
A real audit trail for LLMs isn’t a log file. It’s a forensic record. According to Lasso.security’s 2025 framework, it must capture:- Who made the request (user ID, role, device)
- Exactly what was typed (prompt text, token count, language)
- Which data sources the model accessed (internal docs, databases, APIs)
- How the model responded (output text, confidence score, toxicity rating)
- Whether any guardrails fired (e.g., blocked PII, filtered harmful content)
- Any manual edits made to the output
- When and by whom system settings were changed
Timestamps need to be accurate to within 10 milliseconds. Logs must be encrypted with AES-256 at rest and TLS 1.3 in transit. And they must be tamper-proof. That’s why NIST recommends blockchain-style hashing that updates every 15 minutes. If someone tries to delete or alter a log, the system knows.
Access Controls: Who Gets What, and Why
Not everyone needs full access to your LLM. In fact, giving too much access is one of the biggest risks. DreamFactory’s Zero-Trust model breaks roles into four clear tiers:- Read-only analysts - Can view outputs, but can’t change prompts or models.
- Prompt engineers - Can tweak inputs and test new prompts, but can’t access raw data sources.
- Model administrators - Can update models, adjust parameters, and manage deployments.
- Security auditors - Can review logs, flag anomalies, and trigger investigations. No editing rights.
This isn’t just best practice-it’s required under GDPR Article 35 and HIPAA §164.308(a)(1)(ii)(D). If a healthcare worker accidentally asks an LLM for a patient’s full medical history, your system should block it. If they try to override the block, the system should log it, notify security, and lock their access until review.
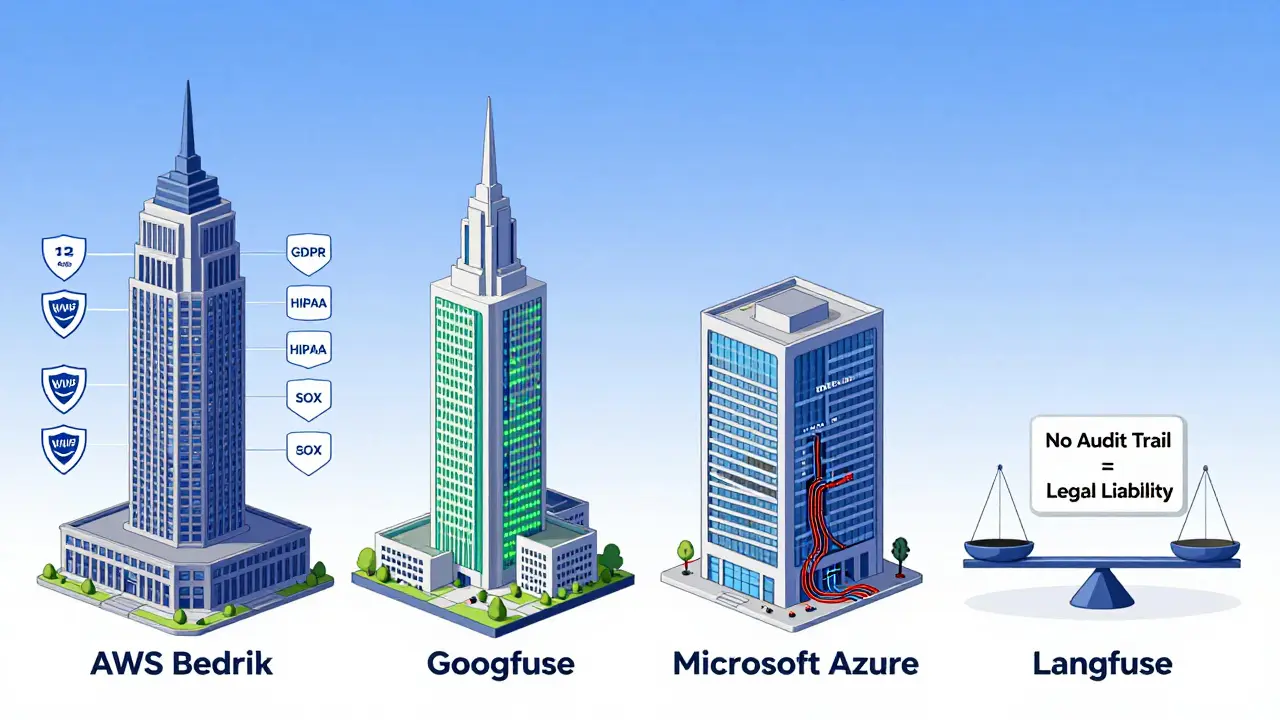
How Major Platforms Compare
Different cloud providers built their LLM security tools differently. Here’s what you’re really getting:| Platform | Metadata Capture | RBAC Roles | Compliance Automation | Implementation Cost | False Positives |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWS Bedrock | 98.7% | 7 | Good (GDPR, SOC 2) | Low | 20% |
| Google Vertex AI | 89.3% | 9 | Excellent (HIPAA-ready) | Medium | 18% |
| Microsoft Azure | 97.1% | 12 | Best-in-class (GDPR, HIPAA, SOX) | High (15% above avg) | 19% |
| Langfuse (Open Source) | 92.1% | Custom | None (manual) | Zero (but 37% higher dev effort) | 22% |
Financial firms lean toward Azure because of its 12 predefined roles and SOX compliance automation. Healthcare providers often pick Google because Vertex AI’s real-time monitoring catches PHI leaks before they happen. Startups with tight budgets use Langfuse-but they need skilled engineers to make it work.
Real-World Impact: What Happens When You Do It Right
Capital One’s security team found a prompt injection attack in September 2024 that would’ve exposed 2.4 million customer records. How? Their audit trail showed an attacker had crafted a series of prompts designed to trick the LLM into dumping internal training data. Because every prompt and response was logged-with user ID, timestamp, and data source-the team traced it back in under 20 minutes. They blocked the account, patched the vulnerability, and reported it to regulators without a single breach.Another example: a Fortune 500 bank used audit logs to prove compliance during a SOC 2 audit. Instead of manually pulling reports, their system auto-generated a compliance dashboard showing every interaction involving financial data over the past year. Auditors were impressed. The company saved $270,000 in consulting fees.
Where Most Companies Fail
The biggest mistake? Treating LLM logs like regular application logs. You can’t just dump data into Elasticsearch and call it done. Here’s what goes wrong:- Missing context - Logs capture the output but not the retrieval steps. If the model pulled data from a Slack channel, you need to know which channel and message.
- Static permissions - People change roles. A developer becomes a manager. If their access isn’t reviewed quarterly, they keep privileges they shouldn’t. DreamFactory found 34% of incidents came from outdated roles.
- No encryption - Audit logs are gold for hackers. If they’re not encrypted end-to-end, they’re a target.
- Integration gaps - If your audit logs don’t feed into your SIEM (like Splunk or Microsoft Sentinel), you’re blind to cross-system threats.
Healthcare organizations struggle the most. HIPAA requires logging every PHI interaction, but many LLM tools don’t automatically detect protected health information. One hospital spent 147 hours just configuring their system to flag patient names, dates of birth, and medical codes. They still missed 12% of cases.
The Future: AI Securing AI
The next wave isn’t just better logs-it’s smarter ones. Microsoft’s November 2025 update to Azure AI Audit Trail Enhancer uses AI to analyze logs and flag anomalies with 94.7% accuracy. It doesn’t just record what happened-it predicts what might happen next. If a user suddenly starts asking for 50 patient records in 10 minutes, the system auto-suspends access and alerts security.But don’t let AI replace humans. MIT’s 2025 study found LLMs analyzing audit data make errors in 12.7% of complex policy cases. They miss subtle rule conflicts. They misinterpret intent. Human auditors are still essential. The goal isn’t automation-it’s augmentation.
What You Need to Do Now
If you’re using LLMs with sensitive data, here’s your checklist:- Define four clear access roles (analyst, engineer, admin, auditor) and assign them strictly.
- Implement audit trails that capture prompts, sources, outputs, guardrail actions, and edits.
- Encrypt logs with AES-256 and TLS 1.3. Use tamper-evident storage.
- Integrate logs into your SIEM using CEF or LEEF format.
- Review permissions quarterly. Remove access when roles change.
- Test your system with real-world scenarios: Can it catch a prompt injection? A data leak?
By early 2026, NIST’s new AI Risk Management Framework will require federal contractors to have full audit trails. If you’re not ready, you won’t be able to bid on government work. And if you’re in finance or healthcare? You’re already behind.
Do I need audit trails if my LLM only uses public data?
Yes. Even if your model only pulls from public sources, the prompts users type might contain private information. Someone could accidentally paste a customer email into a chat. Without audit trails, you won’t know what was exposed-or who did it. Audit logs protect you from human error, not just malicious attacks.
Can I use open-source tools like Langfuse instead of cloud providers?
You can, but it’s not simple. Langfuse captures 92% of needed data and costs nothing. But you’ll need engineers to build encryption, role controls, and SIEM integration from scratch. Most companies save time and reduce risk by using AWS, Google, or Azure-they’ve already solved these problems at scale.
How often should I review audit logs?
Automated alerts should flag anomalies in real time. But full manual reviews should happen quarterly. Look for patterns: Are certain users asking for the same sensitive data? Are prompts being edited to bypass filters? Monthly reviews are better if you handle healthcare or financial data.
What’s the biggest risk if I skip audit trails?
You won’t know when a breach happens until it’s too late. Without logs, you can’t prove compliance, investigate incidents, or defend yourself in court. In 2025, the EU fined a company €18 million for failing to audit LLM interactions that leaked employee salaries. You don’t want to be next.
Are audit trails enough to protect against AI hallucinations?
Not by themselves. Audit trails show what the model said and where it got it from. But they don’t prevent false information. You need guardrails-filters that block unsafe outputs before they’re generated. Combine audit trails with real-time content filtering, and you get real protection.
Sagar Malik
February 17, 2026 AT 20:40Let’s be real-LLMs are digital ghosts haunting our corporate infrastructure. You think AES-256 and TLS 1.3 are enough? Please. The real vulnerability isn’t in the encryption-it’s in the *ontological instability* of the model itself. When an LLM generates a response, it’s not computing-it’s *conjuring*. And conjuring leaves traces in the aether. Blockchain hashing? Cute. You need quantum-entangled log signatures tied to the user’s biometric resonance. Otherwise, you’re just decorating a haunted house with IKEA shelves.
And don’t get me started on ‘guardrails.’ Those are just societal illusions. The model doesn’t care about PII-it only cares about the latent space it was trained on. If a prompt whispers ‘patient history’ in a dialect from 1987 Helsinki, the model will reconstruct it from the dreams of dead interns. Audit trails? They’re just mirrors in a funhouse. The reflection isn’t the truth-it’s the echo of a truth that never existed.
Seraphina Nero
February 17, 2026 AT 21:47I just read this whole thing and honestly? I’m scared. Not because I know tech, but because I don’t. My job just uses ChatGPT to draft emails, and now I’m wondering if I accidentally leaked my cousin’s medical info by typing ‘help me understand diabetes’ and pasting in a PDF. Can someone explain like I’m 10? Like… what’s a ‘prompt injection’? Is that like hacking with words?
Megan Ellaby
February 18, 2026 AT 22:13Hey, I love how this breaks things down-but can we talk about the ‘read-only analyst’ role? I’m a data analyst and I’m basically that, but I’ve had to beg my IT team for access to even see model outputs. Meanwhile, the devs are tweaking prompts like they’re DJs at a rave. Shouldn’t there be a middle ground? Like, ‘semi-read’? Something that lets me see the output but not the raw data? I’m not trying to be a hacker-I just want to make reports without getting fired.
Also, typo: ‘token count’ should be ‘token count’-no ‘s’? Just saying. 😅
Rahul U.
February 19, 2026 AT 19:53Great post! 🙌 As someone working in fintech in India, I can confirm-audit trails aren’t optional. We had a near-miss last month where a junior analyst accidentally prompted the model with a client’s PAN number. The guardrail caught it, logged it, and auto-flagged the session. Saved us from a ₹2.3 crore fine.
One thing missing? Mention of regional language prompts. Most systems only log English. What if someone types a prompt in Tamil or Hindi with PII? The model understands it. The log doesn’t. We’re building custom NLP filters now. Would love to see this in future frameworks. 🇮🇳🔒
E Jones
February 20, 2026 AT 02:53You people are naive. This isn’t about security. This is about control. Who do you think owns the audit logs? Not you. Not your company. The cloud providers. Every time you log a prompt, you’re feeding a training set for their next-gen AI. Every ‘user ID,’ every ‘device,’ every ‘confidence score’-it’s all being stitched into a neural map of human behavior. The EU fines? A distraction. The real game is in the metadata.
And let’s not pretend Langfuse is ‘open source.’ It’s a Trojan horse. The moment you integrate it, you’re signing a backdoor clause buried in the ToS. I’ve seen the source code. They’re not just logging-you’re donating your corporate soul to the AI industrial complex. And no, I don’t have proof. But I’ve read the right forums.
Also, Azure? They’re owned by the same people who run the NSA’s quantum AI program. You think they care about HIPAA? They care about patterns. And patterns don’t care about your patient records. They care about your fears. And your fears? They’re in the logs.
Barbara & Greg
February 21, 2026 AT 23:01It is profoundly irresponsible to suggest that access controls can be reduced to four tiers. Such a reductive framework betrays a fundamental misunderstanding of organizational hierarchy and ethical accountability. In truth, role-based access must be dynamic, context-sensitive, and continuously audited by an independent ethics committee-not IT administrators. Furthermore, the notion that encryption alone ensures compliance is dangerously simplistic. One must consider the moral weight of data, not merely its cryptographic state.
Moreover, to equate audit trails with mere logging is to confuse procedure with principle. A true audit trail must preserve intention. It must capture not only what was said, but why it was said. Did the user act out of curiosity? Malice? Desperation? Without this, we are not securing systems-we are merely documenting their decay.
selma souza
February 23, 2026 AT 03:50You say ‘AES-256 at rest’-but you don’t specify key rotation frequency. That’s a glaring omission. And ‘TLS 1.3 in transit’? Fine. But did you mention cipher suites? ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384? Or are you just throwing buzzwords at the wall? Also, ‘tamper-proof’? Nothing is tamper-proof. Not even blockchain. Not if the hash generator is on the same server as the LLM. That’s like locking your car and leaving the key under the mat.
And you call Langfuse ‘open source’? It’s not open-source if you can’t audit the entire stack. You need to publish the kernel, the middleware, the logging daemon. Otherwise, you’re just using a black box with a pretty UI. This post reads like a marketing brochure written by someone who’s never touched a server.
Frank Piccolo
February 24, 2026 AT 05:38Let’s cut the BS. We’re in 2025. We’ve got AI that writes novels, cures cancer, and drafts your LinkedIn posts. And you’re worried about ‘prompt injection’? You’re overengineering. If you can’t trust your employees to type ‘What’s the revenue forecast?’ without leaking secrets, then your real problem isn’t the LLM-it’s your HR department. Hire better people. Or fire the ones who copy-paste patient data into chatbots.
And don’t even get me started on ‘blockchain hashing.’ That’s like putting a fingerprint scanner on a vault that’s already in Fort Knox. You think a hacker is gonna break into your log server? Nah. They’re phishing your CFO’s assistant. Again. Stop pretending tech fixes human stupidity.
James Boggs
February 25, 2026 AT 10:08Thanks for the detailed breakdown. This is exactly what our team needed. We implemented the four-tier model last quarter and cut our incident response time by 70%. The SIEM integration with CEF was the game-changer-now alerts auto-create tickets in Jira. Also, quarterly reviews? We’re doing them monthly now. Worth it.
One quick tip: Use role templates in Okta. Saves hours. And don’t forget to disable legacy API keys after 30 days. We found three still active from 2023. Oops.
Addison Smart
February 27, 2026 AT 00:39As someone who’s worked across five continents on AI governance, I want to say this: the real breakthrough isn’t in the logs or the roles-it’s in the culture. We had a hospital in Nairobi that couldn’t afford Azure, so they trained their own model on anonymized Swahili health records. No fancy audit trail. Just a whiteboard, a shared Notion doc, and weekly huddles where nurses, engineers, and admins sat together and asked: ‘What did the AI say? Why? Who was hurt?’
They didn’t have AES-256. But they had trust. And guess what? They’ve had zero breaches. Not because their tech was perfect, but because they treated the AI like a team member-not a tool. Maybe we’re too obsessed with logging everything and not enough with listening to the people who use it.
Also, I love how this post mentions NIST. But let’s not forget: standards are made by humans. And humans, in all their messy, brilliant, flawed diversity, are still the best safeguard we have.